Technology: Data storage, backup & retrieval
The unique way UserBridge stores user data and enables GDPR compliant data management and erasure is at the very heart of the data storage model.
Traditional data storage and backup
Traditionally, data backup is fairly trivial process which involves taking a complete export of a database, and/or copying data files. These backups contained a mix of data, such as system/internal, business and customer/user data.
The data relating to people is held together with no practical way to isolate and delete backed-up data pertaining to a particular individual. Backups are created on a daily basis and commonly even more frequently resulting in hundreds or thousands of copies of personal data. Therefore the job of being able to isolate and erase all data belonging to a specific individual within an organization becomes practically impossible.
This approach very likely not to be compliant with GDPR data protection laws, especially regarding the "right to be forgotten".
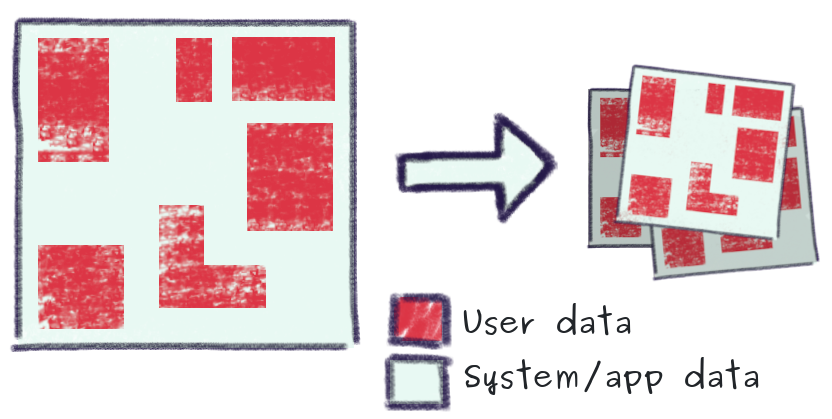
As illustrated, with a traditional backup approach, personal/sensitive data (red) is mixed across the entire data system and is exported in the same "plain text" format in which it is held in primary databases.
UserBridge data storage and backup
The custom-built UserBridge data model is far more sophisticated, providing not only separation of user data from system/application data, but segregation of data relating to individual users, whereby each user is issued an industrial strength randomly generated encryption key which is used to strongly encrypt all data relating to that individual.
At the same time, the UserBridge data model is designed for high performance, flexibility and scalability.
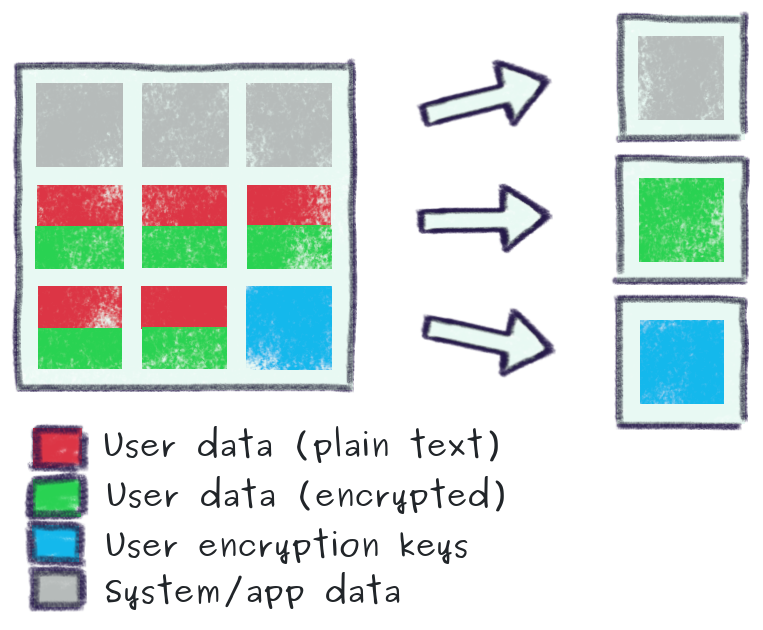
Importantly, plain-text data that is vital for service operation is never exported for backup - only encrypted user is backed-up. This is a critical design feature that facilitates GDPR requirements such as the "right to be forgotten" by simply erasing the encryption key belonging to a particular individual (by doing this, all backed-up encrypted data pertaining to this user is permanently irrecoverable).